Computer vision - Data used at best
For the longest time, humans have hoped to develop machines with human intelligence — essentially creating systems that can act and think like us. Computer Vision (CV) is one such technology where humans have tried to enable computers to interpret digital photographs and videos the way humans do.
Computer Vision is one of the most powerful branches of Artificial Intelligence. It is a field of computer science that focuses on duplicating parts of the complexity of the human visual system. With rapid advancements in AI, deep learning, and neural networks, computer vision has progressed at an incredible pace.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is a field of study focused on enabling computers to see and interpret visual content in a way similar to humans.
It is a multidisciplinary domain that falls under artificial intelligence and machine learning. It uses general learning algorithms along with specialized techniques to extract visual information from images and videos, analyze it, and make meaningful decisions using software algorithms.
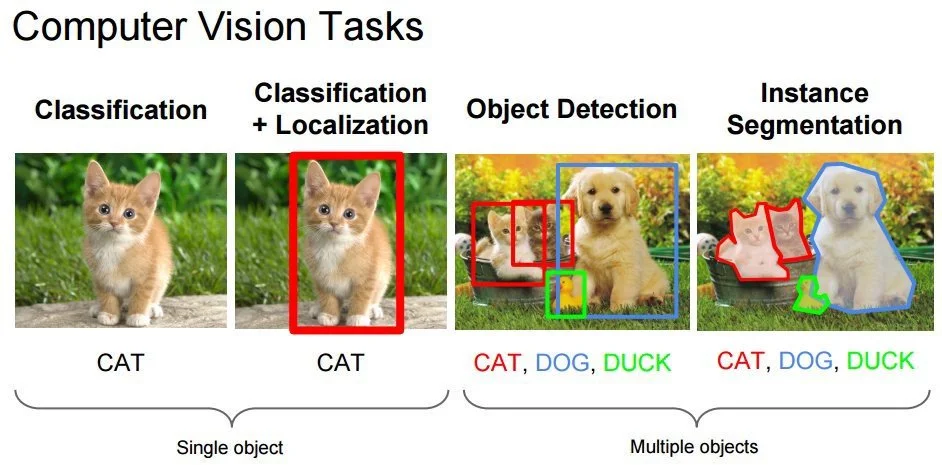
What can Computer Vision do?
Computer Vision can be applied to a wide range of real-world tasks, including:
- Object Identification — Identifying objects in images or videos, such as detecting a specific type of car.
- Object Verification — Determining whether a particular object is present in a visual input.
- Object Classification — Categorizing objects into predefined groups.
- Object Tracking — Tracking one or more moving objects across video frames.

How does Computer Vision work?
Computer Vision is inspired by the way the human brain processes visual information. One of the biggest challenges in both neuroscience and machine learning is understanding how the brain interprets what we see.
The core hypothesis behind computer vision systems is that the human brain relies on patterns to decode objects. Similarly, computer vision algorithms are built on pattern recognition.
Computers are trained on massive volumes of visual data. Images are broken down into pixels, where each pixel holds a numerical color value. The system processes these pixel values, labels objects, identifies patterns, and learns to recognize them accurately over time.
Computer Vision Applications
Augmented and Mixed Reality
Computer vision enables devices to overlay virtual objects onto real-world imagery. Augmented Reality systems use computer vision to detect real-world surfaces such as floors, walls, and furniture, allowing virtual elements to be placed accurately.
Self-Driving Cars
Computer Vision plays a critical role in autonomous vehicles. Cameras capture real-time video from multiple angles and feed it into computer vision software. The system detects roads, traffic signs, vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles, allowing the car to navigate safely.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition systems use computer vision algorithms to detect and analyze facial features in images. These features are compared against databases for authentication, social media tagging, and law enforcement applications.
3D Computer Vision
While traditional computer vision works with 2D images, 3D computer vision adds depth perception. It allows systems to understand spatial relationships and human activity, such as identifying whether a person is walking, standing, or performing an action.
The Road Ahead
Computer vision solutions are already transforming industries ranging from autonomous transportation to healthcare and agriculture. While progress has been remarkable, fully replicating human vision remains a complex challenge.
As computer vision continues to evolve and break new ground across industries, we can expect even greater innovation and adoption in the years to come.
Stay tuned to our blog to discover more complex technologies explained in a simple and practical way.